Unlocking the Power of EMS: How Electrical Muscle Stimulation Works
How Does EMS Work?
Ever ponder the magic behind EMS, transforming electric pulses into robust muscles? This technology employs gentle currents to induce muscle contractions, akin to a workout stimulus your body cannot overlook. It’s as if your brain instructs your muscles to lift a weight, but EMS intensifies this signal, engaging up to 90% of muscle fibers within 20 minutes. This level of intensity is 20 times greater than conventional weight training, as substantiated by German Sport University Cologne studies.
Consider EMS a pathway to achieving fitness goals more swiftly. The miha bodytec system, a vanguard in EMS technology, employs electrode straps and vests to focus on arms, legs, and glutes. An impressive 70% of users report achieving their fitness objectives, even with brief sessions. But what exactly is the Electrical Muscle Stimulation mechanism? It transmits signals that circumvent the brain’s typical constraints, stimulating fast-twitch fibers often neglected during standard exercise.
Spanning decades, from its inception in the 1950s to its current applications in cardiac rehab and sculpting abs with the Slendertone Abs 8, EMS remains enigmatic to many. This guide delves into the science, safety, and the transformative impact of 20-minute sessions on your fitness regimen. Are you prepared to uncover how Electrical Muscle Stimulation explanation can redefine your health journey?
Key Takeaways
- EMS activates up to 20x more muscle intensity than traditional workouts.
- Over 70% of users achieve fitness goals with regular sessions.
- Systems like miha bodytec use vests and straps to target key muscle groups.
- Proven effective for decades, EMS aids in both rehab and fitness, from cardiac therapy to muscle toning.
- Sessions lasting just 20 minutes can rival the benefits of hours spent at the gym.
Introduction to EMS Technology
Ever ponder the role of EMS technology in the realms of athletics and rehabilitation? Let’s dissect it. At its essence, EMS technology employs safe electrical signals to stimulate muscles, acting as a personal fitness assistant. These impulses replicate nerve signals, inducing muscle contractions without the need for physical exertion. The process is facilitated through electrode pads on the skin, transmitting controlled pulses that engage up to 90% of muscle fibers in a single session. This is why a mere 20 minutes of EMS can rival hours of conventional training.
Definition and Purpose of EMS
EMS devices aim to boost strength, accelerate recovery, and alleviate pain. Envision a tool that empowers stroke survivors to regain mobility or enables athletes to fit in a workout amidst a hectic schedule. Its adaptability positions it as a transformative technology. Physiotherapy professionals attest to EMS’s efficacy in post-stroke rehabilitation, pain management, and post-surgical recovery.
Brief History of EMS Development
- 1960s: EMS begins in hospitals, aiding in muscle re-education for paralysis and post-op patients.
- 1980s: Early devices receive FDA approval for pain relief, sparking interest in non-medical applications.
- 2000s–Present: Consumer-friendly EMS technology emerges, merging medical origins with fitness trends. Today, devices like the L(A)B EMS system focus on fitness objectives, backed by studies confirming its effectiveness in ACL rehabilitation and athletic performance.
From clinical settings to fitness centers, EMS has undergone significant transformation. Yet, its fundamental objective remains unchanged: to enhance bodily function, expedite healing.
The Science Behind EMS
Ever ponder, “How does EMS work?” Let’s dissect it: your muscles react to electrical signals from your nervous system. The Electrical Muscle Stimulation mechanism leverages this by transmitting gentle pulses through electrodes, mimicking your body’s natural signals. These currents induce EMS muscle contractions, effectively simulating a workout for your muscles without physical exertion. It’s akin to nudging your muscles to “awaken” and engage actively.
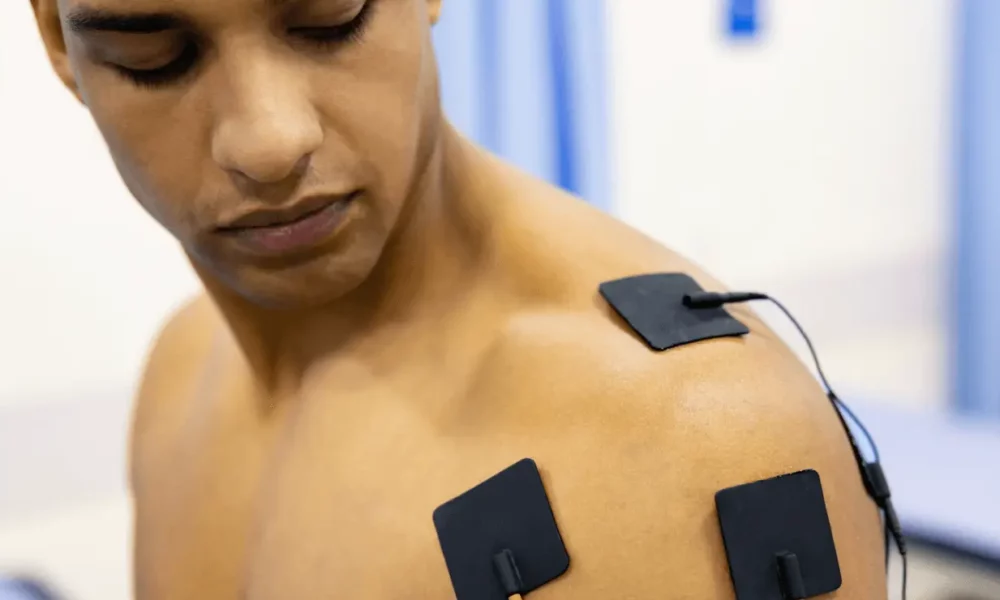
Electrodes serve as the conduit between the device and your muscles. They manifest in various forms, such as adhesive pads or advanced, tech-integrated clothing. Their primary function is to direct signals to precise areas, akin to a painter selecting the right brush size. Inaccurate placement can lead to missed targets, but correct alignment elicits robust muscle engagement. High-grade electrodes guarantee consistent, uniform signals, eliminating any weak points.
Seeking real-world evidence? A 2019 study demonstrated EMS’s efficacy in augmenting muscle strength post-knee surgery. When combined with physical exercise, EMS can significantly enhance muscle development. For insights into weight loss, refer to this analysis on calorie expenditure and dietary integration.
In summary, EMS communicates with your body’s language. By replicating your nervous system’s signals, it transforms passive recovery into active muscle growth. With the appropriate electrodes, you’re not merely utilizing technology; you’re collaborating with your body’s inherent capabilities.
How EMS Devices Are Used
EMS devices serve various purposes, from improving fitness to aiding in recovery and pain management. Their functionality is tailored to meet individual needs. Here’s a closer look at their practical applications:
Common Applications of EMS in Fitness
For those dedicated to fitness, EMS training offers unique benefits. It allows for muscle toning during everyday activities, such as walking or cooking. Research indicates that athletes can achieve strength gains comparable to traditional workouts1. Many devices integrate with apps, providing customized workout plans. For instance, runners might benefit from high-intensity pulses, while yogis might focus on core exercises. It’s important to note, though, that EMS should complement, not replace, physical activity.
EMS in Physical Rehabilitation
In the realm of physical rehabilitation, EMS plays a significant role in strengthening muscles post-injury. Therapists employ EMS to mimic natural muscle contractions, aiding in muscle re-education after surgery or stroke. The FDA has cleared devices like Slendertone Flex for use in rehabilitation settings2. It’s essential to use only FDA-cleared devices for safety. Research supports its effectiveness in preventing muscle atrophy during recovery. Always consult a healthcare professional before initiating EMS therapy.
EMS for Pain Management
EMS can also be used to manage pain by interrupting pain signals. This method has been reported to reduce reliance on pain medication. It’s important to note, though, that safety is a priority. The FDA has issued warnings about unregulated EMS devices that can cause burns or shocks3. Always verify that any device you purchase is FDA-cleared.
Types of EMS Devices
Choosing the right EMS device can be daunting with the multitude of options available. We will explore the three primary categories to assist you in selecting the technology that aligns with your objectives. Whether your aim is post-workout recovery or achieving full-body toning, grasping these distinctions is critical.
Handheld EMS Units
Handheld devices, such as the Compex Sport, employ EMS device functions to concentrate on specific muscle groups. Their wired pads enable precise targeting of areas like calves, shoulders, or hamstrings. Ideal for home use, these devices often come with preset programs designed for recovery or endurance enhancement. For instance, the Compex Sport offers 10 programs tailored for marathon training to injury rehabilitation. Their portability makes them a preferred choice for both athletes and novices.
Wearable EMS Technology
Wearable technology elevates EMS technology to a new level. Brands like Compex Wireless provide wireless pads or smart garments that allow for unrestricted movement during sessions. These devices connect to apps for tracking progress and intensity adjustments. The Compex Wireless, for example, links to your phone, guiding you through over 10 recovery and strength programs. They are perfect for those with busy schedules, ensuring convenience without compromising on effectiveness.
Professional EMS Machines
Clinical-grade machines employ advanced muscle stimulation therapy for serious applications, such as post-surgery rehabilitation. These high-intensity devices necessitate professional supervision, typically found in physical therapy settings or elite athlete facilities. They offer deeper muscle engagement than home models, targeting both Type 1 and Type 2 muscle fibers. For example, studies indicate they enhance vertical jump power and VO2 max when used in conjunction with exercise. Always consult a specialist before selecting this category.
Uncertain about your choice? Begin with a handheld unit for targeted recovery support or opt for a wearable device for daily use. Always verify FDA clearance labels and consult reviews to ensure safety and efficacy. Your muscles deserve technology that aligns with your objectives—no need for guesswork.
The Benefits of Using EMS
Imagine the possibility of building muscle at an unprecedented rate—EMS training unlocks the power to engage up to 90% of your muscle fibers in a single session. This technology is not just for those seeking muscle toning or rehabilitation; it is a scientifically-backed solution for achieving fitness goals. Let’s explore what sets it apart as a transformative tool.
Enhanced Muscle Strength and Tone
EMS workout effectiveness is evident in its ability to enhance muscle strength and tone. Those 20-minute sessions are not just any workout; they induce 36,000 muscle contractions, surpassing the impact of traditional weightlifting. A 2016 study demonstrated that EMS users experienced a 15% increase in squat strength compared to those using traditional training methods. With no need for equipment, it targets deep muscles often overlooked in conventional gyms. Brute Suits notes its effectiveness in building core strength while safeguarding joints, making it a preferred choice for post-pregnancy rehabilitation or alleviating the stiffness associated with desk jobs.
Improved Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Reduced muscle soreness by 40% post-surgery using EMS
- Physical therapists use EMS to restore movement in stroke survivors
- Stimulates blood flow to injured areas, speeding healing
Safety Considerations When Using EMS
Before engaging in EMS sessions, it is imperative to ensure safety. How does EMS work? begins with comprehending EMS device functions and adhering to safety limits. This approach safeguards both the user and their body from harm.
Who Should Avoid EMS Treatments
EMS is not suitable for all individuals. The Electrical Muscle Stimulation explanation reveals it poses risks for those with specific conditions. These include:
- Heart conditions (pacemakers, ICDs, or arrhythmias)
- Pregnancy (consult a doctor first)
- Severe skin conditions or open wounds
- Epilepsy or neurological disorders
Guidelines for Safe EMS Usage
To ensure safety, follow these guidelines:
- Start low, go slow: Initiate with the lowest intensity setting. Allow your body time to adjust—there is no need to rush.
- Clean is key: Ensure electrodes are clean before and after use. Dirty pads can lead to infection.
- Hydrate first: Dehydration combined with EMS can cause muscle cramps. Drink water before beginning a session.
- Check device manuals: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for electrode placement and session duration (30 minutes max per session, as recommended by experts).>
If you remain uncertain, consult a healthcare provider. Safety transcends a checklist; it embodies a mindset. Approach EMS with caution, stay informed, and utilize it as a tool for empowerment, not endangerment.
Integrating EMS into Your Fitness Routine
Ready to incorporate EMS into your workout regimen? We’ll guide you through it step by step, ensuring no confusion. EMS workout effectiveness is maximized when used with purpose. Begin with a modest approach, be patient, and allow your body to adjust.
Recommendations for Beginners
- Start with 1-2 sessions per week, each lasting 20–27 minutes. Balance these with lighter days to prevent overexertion.
- Begin with major muscle groups: quads, glutes, and back. Utilize devices like Compex’s FIT range for full-body engagement, easing you into the practice.
- Gradually increase intensity. Pay attention to your body’s signals—EMS training benefits, such as reduced recovery time, indicate rapid progress.
Comparing EMS with Other Technologies
When selecting technology for your fitness objectives, it’s essential to comprehend EMS’s position within the broader spectrum of muscle stimulation therapies. This comparison will illuminate its unique role among other options.
“EMS technology delivers targeted EMS muscle contractions, unlike TENS units which focus on pain relief.”
Let’s dissect the distinctions:
- TENS units aim to interrupt pain signals by targeting nerves, whereas EMS directly stimulates muscles to enhance strength.
- WB-EMS surpasses vibration platforms in muscle activation—research indicates that 20-minute sessions are equivalent to traditional 2x weekly resistance training.
- Electrostimulation belts focus on specific areas, such as the abdomen, whereas WB-EMS engages entire muscle groups across the body.
Studies have documented tangible outcomes:
- A 16-week study revealed that WB-EMS users experienced 7% leg strength increases, compared to 12.7% for traditional training, yet required fewer weekly sessions (1.5 vs 2).
- EMS training alone boosted power output by 29%, demonstrating its superiority over isolated methods.
What about integrating different technologies? Many Pilates studios now combine EMS suits with Reformer machines, illustrating the synergy between various technologies. Even fitness trackers? They monitor data but cannot substitute EMS’s direct muscle stimulation.
It’s important to remember: EMS is not meant to replace all other methods—it’s a tool for intensifying muscle engagement. For those with limited time, WB-EMS offers results in half the time of traditional workouts. Yet, it’s vital to align it with your specific goals. Your muscles and routine deserve the optimal combination.
Future Trends in EMS Technology
Envision a future where EMS technology dynamically adjusts to your body’s needs in real-time. Innovations such as AI-powered devices that modify EMS workout effectiveness based on muscle fatigue or recovery phases are currently under development. The introduction of wireless electrode systems and app-linked controls heralds a new era of convenience, enabling effortless tracking of progress. Research from the Journal of Emergency Medical Services indicates that these advancements will render EMS tools more intelligent and tailored than ever before.
Smarter Devices, Better Results
Future EMS technology will prioritize precision. Envision electrodes that pinpoint specific muscle groups with unparalleled accuracy, eliminating the need for guesswork during EMS muscle contractions. Biometric feedback systems will soon integrate real-time data with trainers or healthcare providers, ensuring each session is perfectly tailored. Despite hurdles such as cost and cybersecurity, entities like BruteSuits are pioneering prototypes that harmonize innovation with safety.
EMS in Elite Sports and Daily Life
Professional athletes are at the forefront of adopting EMS technology—think cyclists leveraging it to enhance endurance or sprinters refining explosive power. The American Heart Association’s 2021 study demonstrates the efficacy of EMS-driven protocols in accelerating recovery post-injury. Yet, this technology extends beyond elite athletes. As FEMA emphasizes, investing in EMS technology could expedite emergency care and enhance disaster response capabilities. For the average user, it promises workouts that align with personal goals, whether for injury rehabilitation or fitness achievements.
As technology advances, so does its transformative power. Will EMS become as ubiquitous as a gym membership? The Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts an uptick in EMS-related job opportunities, signaling a burgeoning field. Remain inquisitive—what is being explored in labs today may redefine how we train, recover, and perform in the future.

Source: Unlocking the Power of EMS: How Electrical Muscle Stimulation Works